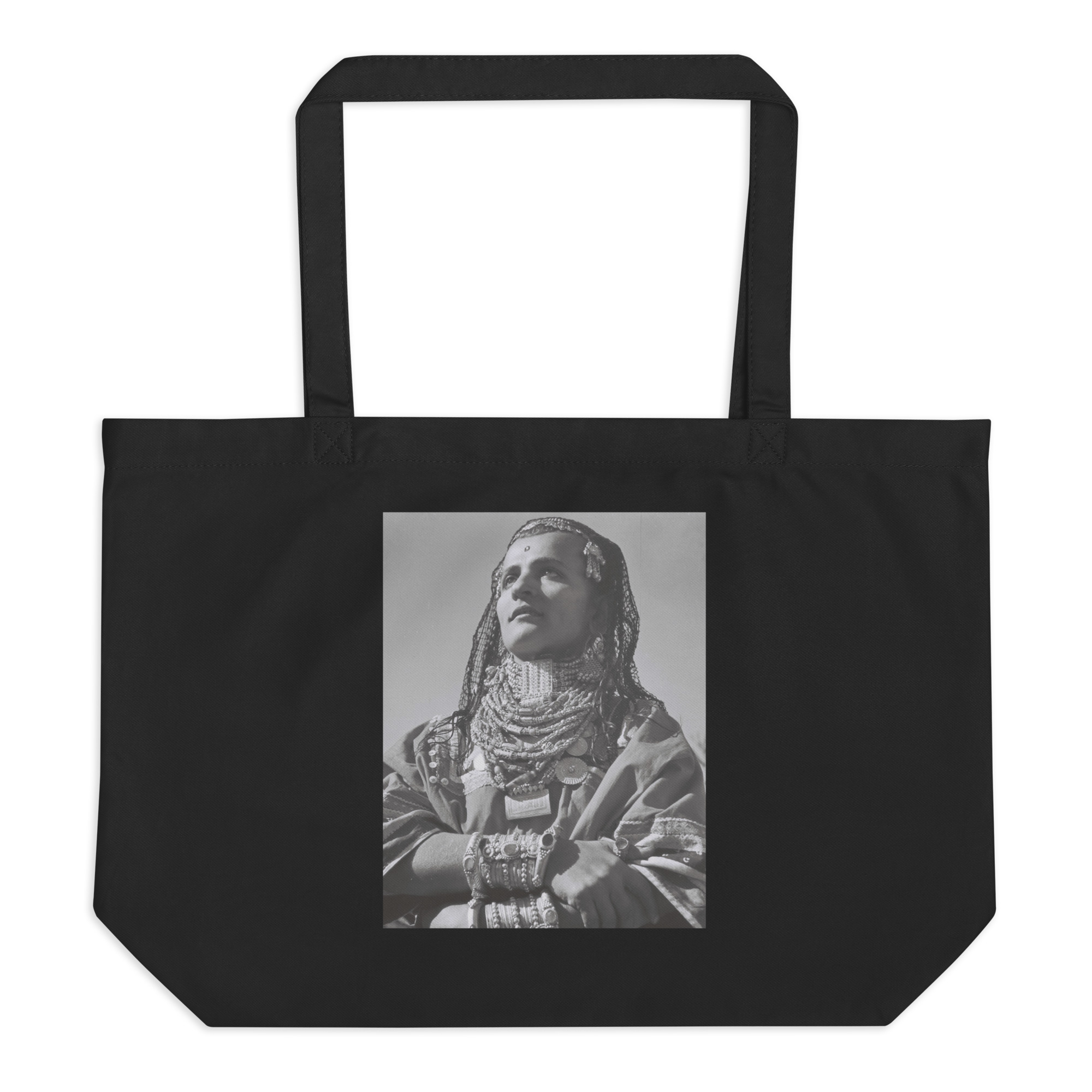
Religion

Concubine of a Levite: Midrash and Aggadah
The story of the concubine at Gibeah, who is murdered when her husband sends her out to a crowd of Benjamites, is one of the most shocking narratives in the Bible. The rabbis do not blame the unnamed woman for her fate and the ensuing crisis, instead placing the blame at the feet of the Levite and the leaders of Israel.

Conservative Judaism in the United States
Women have played a pivotal role in propelling the Conservative Movement to confront essential issues including Jewish education and gender equality. The Movement’s attention to issues such as the religious education of Jewish girls, the status of the agunah (deserted wife), equal participation of women in ritual, the ordination of women, and innovations in liturgy and ritual to speak to women’s experiences has helped to shape the self-definition of Conservative Judaism, and has enabled talented Jewish women to reach new heights in religious leadership.
Contraception
One of the major Jewish sources dealing with contraception is Tosefta Niddah. As with the issue of abortion, the more public the debate about contraception became over time, the more some rabbinic authorities attempted to usurp women’s control over their bodies.
Conversas
After the establishment of the Inquisition in 1478, observance of crypto-Judaism became dangerous and more difficult. Women were at the center of Judaizing efforts, since the home was the only remaining institution in which one could observe Jewish law. Crypto-Jewish women most frequently observed the Sabbath and dietary laws.
Creation According to Eve: Beyond Genesis 3
No feminist critic of the Bible has neglected to discuss the story or stories of the creation of woman; yet, despite significant differences in theoretical approach and focus, their readings generally have been confined to Genesis 1–3. Beyond Genesis 3, the matter of creation and femininity is addressed, offering new and complex insights.

Helen Miller Dalsheimer
Helen Miller Dalsheimer was a leader in the Jewish community, both nationally and in her native Baltimore. She had a distinguished career as a volunteer, helping lead organizations such as the National Federation of Temple Sisterhoods and the Women’s Hospital of Baltimore.

Rabbi Michelle Dardashti
Rabbi Michelle Dardashti currently serves as the Rabbi of Brown RISD Hillel and Associate University Chaplain for the Jewish Community at Brown.

Daughter of Jephthah: Bible

Daughter of Pharaoh: Midrash and Aggadah
The rabbis depict the daughter of Pharaoh, who rescued the baby Moses, as a righteous figure who did not follow her father’s wicked ways but rather converted and ceased worshiping idols. She was highly praised by the Rabbis, and the midrash includes her among the devout women converts and those who entered the Garden of Eden while still alive.

Daughter Zion (Bat Tzion)
“Daughter Zion” or “Fair Zion” (in Hebrew bat tzion) is the personification of Jerusalem in poetic and prophetic literature. Initially, the city is positively likened to a daughter, protected under God’s special regard, but later, under the Babylonian siege, she is devastated, even ravaged. However, when Jerusalem is rebuilt, the daughter is forsaken no longer, returning to God’s grace in the prophecies of consolation.

Daughters of Lot: Bible
When the men of Sodom demand sexual relations with two messengers from God, Lot offers his daughters instead. The daughters, however, escape with Lot and live in a cave after Sodom is destroyed. There they have relations with their father and give birth to his sons.

Daughters of Zelophehad: Bible
The story of the five daughters of Zelophehad provides legitimation of a limited right of Israelite women to inherit land. The story celebrates women’s boldness and at the same time offers comfort for men who have the misfortune (from the Bible’s androcentric point of view) to have no sons.

Daughters of Zelophehad: Midrash and Aggadah
The midrash rains many praises on the daughters of Zelophehad, describing them all as equally wise and virtuous, as well as exegetes. The midrash also says that they are mentioned by the Patriarchs and are so righteous that they are blessed with children despite their old age.
Annette Daum
A deeply religious feminist, Annette Daum dedicated her life to two causes: interfaith dialogue and feminism. Among other leadership positions, she coordinated interreligious affairs at the Union of American Hebrew congregations, edited the journal Interreligious Currents, and organized various task forces focused on gender equality and Jewish-Christian feminist dialogue.

Carrie Dreyfuss Davidson
Carrie Dreyfuss Davidson became an important voice for women in the Conservative Movement as a founder of United Synagogue’s Women’s League and founding editor of its journal Outlook. Davidson exemplified the often-competing paradigms of Jewish homemaker and accomplished writer and community leader.
Deborah 1: Midrash and Aggadah
Rebekah’s nurse Deborah died when Jacob was on his way to the Land of Canaan, close to Bethel, where she was buried under a tree. The rabbis describe her as having a close relationship to Jacob.

Deborah 2: Midrash and Aggadah
Deborah, one of the most extraordinary women in the Bible, is presented as an extremely righteous and praiseworthy woman in rabbinic literature. Though some traditions criticize her pride, perhaps wary of how she transgressed gender norms, most of the rabbinic texts about Deborah are filled with praise.

Deborah: Bible

Delilah: Bible

Delilah: Midrash and Aggadah
The midrashim on Delilah attest to the negative attitude of the Rabbis toward non-Jewish women. The Rabbis accentuated the negative aspects of the relations between Samson and Delilah in order to demonstrate the havoc that a foreign woman could wreak.

Anita Diamant
Anita Diamant is a novelist, feminist, and liberal Jew who has written five novels, the best known of which is The Red Tent (1997), made into an American television miniseries (2014). She is the author of many books Jewish self-help books, the best known of which is The New Jewish Wedding. She is the founding president of Mayyim Hayyim, the Living Waters Community Mikveh and Education Center.

Dinah: Bible

Dinah: Midrash and Aggadah
Dinah was the only daughter of Jacob and Leah, and the Rabbis present her as possessing many positive qualities, as was fitting for the daughter of the progenitors of the Israelite nation. The rabbis also offer many different explanations for the rape of Dinah, trying to understand the troubling story.
Divorce: The Halakhic Perspective



