Jeanette Wolff
A well-known Social Democrat and Holocaust survivor committed to equal rights for women and sustained Jewish existence in Germany, Jeanette Wolff refused to compromise her socio-political beliefs. She was active in the SPD both before and after the war and served on the denazification committee in post-war Berlin .

Marguerite Wolff
London-born Marguerite Wolff was a member of Berlin’s intelligentsia in the early 20th century. Between 1925 and 1933 she served as unofficial co-director and later as a research scholar at the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Foreign Public Law and International Law.

Nelly Wolffheim
Nelly Wolffheim spent her career developing and teaching a kindergarten curriculum based around Sigmund Freud’s psychoanalytic framework. She taught this curriculum, which encouraged children to express their sexual desires, to Jewish women teachers in Berlin. After escaping Germany for England in 1939, Wolffheim struggled to continue her research but began publishing her work again after the war.

Myra Wolfgang

Theresa Wolfson
Theresa Wolfson, economist and educator, taught at Brooklyn College from 1929 until her retirement in 1967. A prolific writer, she published in the fields of labor economics and industrial relations. As early as 1916, Wolfson studied barriers to the advancement of women in the workplace and the unequal treatment of women within trade unions.
Rosi Wolfstein-Fröhlich
Rosi Wolfstein’s life constituted a battle against war, racism, and social injustice. She worked with other socialist political figures such as Rosa Luxemburg, helped found the Independent Social Democratic Party, and was a representative for the German Communist Party. Despite having to flee to the United Stattes during World War II, Wolfstein returned to Germany and remained active in party and workplace politics until her death.
Martha Wollstein
Responding to the public health crisis of the early twentieth century with a declaration that the current generation of women physicians had “entered societies and laboratories for the benefit of all,” Martha Wollstein had an exemplary career in pathology and the experimental study of childhood diseases.
Woman Wisdom: Bible

Women and Sephardic Music
Ladino or Judeo-Spanish Sephardic songs are primarily a women’s repertoire. The two main traditions are that of northern Morocco and the Eastern Mediterranean, primarily today’s Turkey, Greece, the Balkans.

Women at Masada
In the first century BCE, King Herod the Great built a fortified palace atop the mountain of Masada overlooking the Dead Sea. Seventy years after Herod’s death, during the First Jewish Revolt against Rome, Masada was occupied by bands of Jewish rebels, including families. This entry surveys the literary and archaeological evidence of women among the rebels at Masada.

Women in Israeli Cinema
For many years, women played a secondary role in Israeli cinema, with little voice of their own and limited largely to objects of the male gaze. More recently, women filmmakers, often emphasizing autobiographical narratives, have begun to critique the patriarchal family and present new perceptions of female sexuality and female social roles.

Women in Israeli Music
The arrival in pre- and post-state Israel of Jewish immigrants from Europe, the Middle East, and North Africa resulted in a culturally diverse proliferation of music, much of which involved performance and composition by Jewish women. Jewish women have also contributed significantly to the development of music education and music scholarship, being involved in music studies publications and projects as well as the development of music education institutions.

Women in Samson's Life: Midrash and Aggadah
The three women in Samson’s life were Gentiles: the woman from Timnah, the woman from Gaza, and Delilah. In the midrash, rabbis used Samson’s situation to denounce involvement with foreign women.

Women in the Holocaust
During the Holocaust, many women’s experiences were shaped by their gender. Pre-war roles and responsibilities, anticipatory reactions to Nazi actions, German policy and treatment of men and women, and the responses of Jewish men and women to Nazi persecution all affected women’s ordeals.

Women in the Yishuv Workforce
A review of data and statistics about women in the Yishuv workforce from about 1920 to 1945 show that women’s participation in the workforce correlated with higher levels of economic development. Though women contributed to the growth of an economy in pre-state Palestine, they often faced discrimination in what positions they could take and in their wages.

Women Journalists in Israel
Despite social barriers, Jewish women have played an essential role in the creation and propagation of news and journalism in Israel. With the advent of women’s magazines and the popularization of television, women became particularly involved in the news industry. However, while the numbers of female Israeli journalists have increased, women journalists still face gender-based discrimination. In recent years, many have become vocal members of women’s rights movements such as #MeToo and advocates for a more equitable future.

Women of Solomon: Bible
Solomon, third king of Israel, is said to have had a harem that included 700 wives and 300 concubines. Many of those women were not Israelites and refused to adopt Israelite traditions and religion, reinforcing a common Biblical motif about foreign women.

Women of the Wall

Women Religious Workers in Eastern Europe
In nineteenth- and early twentieth-century Eastern Europe, Jewish women served their communities as spiritual leaders and paid religious functionaries. The main women’s leadership roles documented in Yiddish literature, memoirs, memorial books, and ethnographic studies include the midwife, the evil eye healer, the cemetery measurer, the prayer leader, and the mourning woman.

Women Warriors
In the Hebrew Bible and ancient Jewish literature, most warriors are men. However, a few women go to war or kill: Deborah, Jael, the unnamed woman of Thebez, and Judith.

Women with Hand-Drums, Dancing: Bible
Several biblical passages mention women (e.g., Miriam) celebrating victory with drums, dances, and song. Examining those passages in light of archaeological materials and comparative Near Eastern texts indicates that women, rather than men, were percussionists in ancient Israel and likely participated in religious and secular musical activities.

Women's American ORT
Five years after the American chapter of the Organization for Rehabilitation through Training (ORT) was founded in 1922, a women’s auxiliary group (WAO) was created. WAO aided displaced Europeans and focused on creating vocational schools across the world. In the later twentieth century, WAO expanded to help create medical services for students and provide recreational facilities, among other programs.
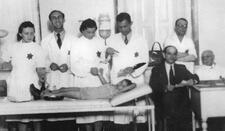
Women's Health in the Ghettos of Eastern Europe
Women in the ghettos of Eastern Europe often outnumbered men, but within ghetto populations, women generally had lower mortality rates than men, perhaps due to their ability to adapt to their surroundings and use of public health services. However, women suffered uniquely; many women did not menstruate, suffered from symptoms caused by hormone imbalances, and endured prohibitions against childbirth.

Women's League for Conservative Judaism
Women’s League for Conservative Judaism (WLCJ), founded in 1918, is the national organization of Conservative sisterhoods. Throughout its history WLCJ has foregrounded women’s education and engagement in order to enrich the spiritual and religious lives of Conservative/Masorti women and to empower them as leaders in their homes, synagogues, and communities.
Women's Studies in Israel
In the 1980s and 1990s, Women and Gender Studies programs were established at the five Israeli Universities, emerging from the “New Women’s Liberation” movement of the 1970s. The programs faced many challenges, especially a lack of university support, but today are popular with students and faculty. Women’s Studies programs also developed at Israeli colleges, and the Israeli Association for Feminist and gender Studies is a national organization of feminist scholars.


