Jewish History: Holocaust
Margarete Berent
Margarete Berent was the first female lawyer to practice in Prussia and the second female lawyer ever licensed in Germany. In 1925 she opened her own law firm in Berlin and, after fleeing Nazi Germany, opened her own firm in the United States. Not only was she the first female lawyer and the head of her own law firm, but she was also an ardent feminist and active in promoting opportunities for women.

Lili Berger
A prolific literary critic and essayist who wrote fiction, short stories, and novels, Lili Berger worked to educate, instruct, expose, and memorialize. Her works captured the Polish-Jewish experience in the twentieth century, particularly those of other writers and artists.

Elisabeth Bergner
Elisabeth Bergner, born in Austrian Galicia, was one of the most successful and popular stage and screen actresses in pre-World War II Germany, known for her superior artistic skills and wide variety of roles. During the war, she helped actors escape Germany. She was honored with the Schiller Prize of the City of Mannheim, the Ernst Lubitsch Prize, and the Austrian Cross of Merit for Science and Art.

Hinde Bergner
Hinde Bergner holds a special place in Yiddish literature by virtue of the fact that her memoir of family life in a late nineteenth-century Galician shtetl is one of few extant Yiddish memoirs to describe the traditional Jewish family on the edge of modernity from the perspective of a woman. Her intimate portrayal of her life results in a valuable source for Jewish social, family, and women’s history.

Cora Berliner
Cora Berliner was an economist and social scientist who held leadership positions in several major Jewish organizations in Germany between 1910 and 1942. These organizations included the Association of Jewish Youth Organizations in Germany, the Reich Representation of German Jews, and the League of Jewish Women.

Clementine Bern-Zernik
A lawyer by training, Vienna-born Clementine Bern-Zernik produced broadcasts for the US Office of War Information in London during the war, served as the director of a Displaced Persons Camp in post-war Germany, and spent the last 50 years of her life as a UN liaison to the New York Public Library. Throughout her life she maintained a strong Austrian identity and was a founding member of the Austrian-American Federation.

Ilse Bing
Ilse Bing was known as the “Queen of the Leica” for her work in photojournalism, fashion, and advertising with this new camera, fast film, and darkroom techniques of polarization and cropping. Her work was highly influential in France in the 1930s when many émigré artists were energized by the cross fertilization of disciplines that contributed to modern photography.

Marietta Blau
German physicist Marietta Blau joined the Institut für Radiumforschung, where she developed an emulsion technique for recording the tracks of particles that allowed her to detect neutrons and observe nuclear disintegration caused by cosmic rays. Forced to emigrate in 1938, worked for the US Atomic Energy Commission and later taught at the University of Miami. Throughout her career, she faced discrimination for her religion and gender and was denied paid work.

Gay Block

Gertrud Bodenwieser
A member of the first generation of modern dancers in Vienna, Gertrud Bodenwieser developed her own style of modern Ausdruckstanz (expressionist dance). From her studio in Vienna, she established the Bodenwieser Dance Group and went on to tour Europe, Japan, and Columbia. In 1938, she immigrated to Australia and played a significant role in the development of modern dance there.
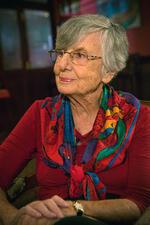
Ruth Bondy
Ruth Bondy was an author, a journalist, and a gifted translator. Born in Prague to a large Zionist family, the majority of whose members perished in the Holocaust, Bondy survived Theresienstadt and Auschwitz-Birkenau and arrived in Israel in late 1948. She soon became a journalist, and eventually began to write biographies and translate from Czech to Hebrew.

Hansi Brand (Hartmann)
Hansi Hartmann started helping escaped Jewish refugees in Hungary with her husband Joel in 1938. She later played a central role in The Relief and Rescue Committee, founded by Joel in 1942, and went on to save thousands of Jews. After the war, she emigrated to Palestine and gave critical testimony at the Kasztner and Eichmann Trials.

Suzanne Brøgger
Suzanne Brøgger is a Danish journalist, cultural critic, author, and essayist. With more than twenty books to her name, Brøgger has received widespread acclaim for her novels, essays, anthologies, poems, and plays.
Rokhel Brokhes
Rohkel Brokhes offered an intimate and poignant glimpse into Jewish family life in Russia in the early 20th century. Her short stories, novellas, and plays documented the often-harsh lives of Russian Jews, especially women. She was born and raised in Minsk, and she would also die there in the ghetto.

Edith Bülbring
German-born scientist Edith Bülbring was renowned for her work in smooth muscle physiology, which paved the way for contemporary cellular investigations. She pursued this work through a large and flourishing large research group at Oxford University, which she led for seventeen years. In 1958 she was elected to the Royal Society.

Judy Cassab
Vienna-born, Budapest-trained painter Judy Cassab, a survivor of the Holocaust, arrived in Australia in 1951. She became one of the country’s best-known and best-loved artists, primarily for her portraits but also for her depictions of Australia’s bright interior.

Central Organizations of Jews in Germany (1933-1943)
During the Nazi regime, the political participation of the League of Jewish Women in the affairs of the Jewish self-help organization the Reichsvertretung was initially unwelcomed by male leaders, despite the fact that women attended its meetings. Following the dissolution of the League in 1938, four of its members created their own network in order to present a united front for Jewish women’s interests and continued to participate in important functions of the Reichsvertretung.

Charlotte Chaney

Charlotte Charlaque
Charlotte Charlaque was a transgender trailblazer, actress, and translator in Weimer Berlin and post-Shoah New York City.

Children's Literature in the United States
Children’s literature in the United States would not be the same without Jewish women. From Sydney Taylor to Judy Blume to Lesléa Newman, Jewish women have written books read by millions of children and teenagers in the U.S. for more than a century.

Cuba

Liza Czapnik
Liza Czapnik was a Polish freedom fighter during World War II who started working against the Nazi occupation after witnessing a mass murder of Jewish people near her hometown. After being interned in the Grodno ghetto, she escaped and began working as a courier for the anti-fascist underground in Bialystok. After the war, she earned a PhD and taught English until 1991, when she made Aliyah and settled in Beersheva.

Modern Dance Performance in the United States
Jewish immigrants to the New World brought with them their ritual and celebratory Jewish dances, but these traditional forms of Jewish dance waned in the United States. Working-class and poor Jewish immigrants parents sought out culture and education in the arts for their children, often as a vehicle for assimilation. Jewish women were particularly attracted to the field of modern dance.

Lucy S. Dawidowicz
Lucy S. Dawidowicz was an American-Jewish historian whose influential and controversial works reflect her deep personal and academic commitment to the Jewish people. She spent time in Poland immediately before the Holocaust and time in Germany immediately after it. Dawidowicz’s works, which received numerous awards, concern American and Eastern European Jewry, and the Holocaust.

Edis De Philippe
Opera in Israel owes its creation primarily to singer, director, producer, and impresario Edis De Philippe. De Philippe made her New York opera debut in 1935 before performing with the Paris Opera and touring Europe and South America. She then founded the Israel National Opera Company in 1947 and ran it until her death in 1979.


