Education

Lillian R. Lieber
Frustrated with the way math is taught in schools, Lillian R. Lieber created unconventional, popular books to excite young readers and incite their curiosity.
Judith Berlin Lieberman
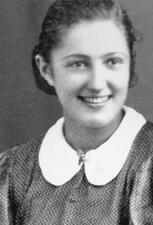
Rivka Kuper Liebeskind
Rivka Liebeskind joined the Akiva Zionist movement as a teenager, becoming a leader in her local chapter and encouraging members to continue their activities after the German occupation began. When the movement transitioned to resistance activities in 1942, she aided young people escaping the Krakow ghetto. Liebeskind survived her deportation to Birkneau and moved to Israel after the war.

Estelle Liebling
Estelle Liebling was a talented opera singer who performed at the Dresden Royal Opera House and the Metropolitan Opera and toured through the United States and Europe. She trained popular and Metropolitan Opera singers at her studio in New York for fifty years and wrote books on vocal training and compositions for piano and voice.

Eliana Light

Belda Lindenbaum
Belda Lindenbaum was driven by the birth of her daughters to create new opportunities for Jewish women and girls.

Deborah Lipstadt
Deborah D. Lipstadt is an American Jewish historian of issues surrounding understanding the Holocaust, ranging from reception of news of the extermination of European Jews to denial of the existence of the Holocaust. Lipstadt achieved renown for her defense against libel brought by David Irving, a British Holocaust denier. Her dramatic trial was transformed into a film starring Rachel Weisz.
Literature Scholars in the United States
Jewish women have been among the key figures in literary scholarship in the United States in the postwar period. Those entering the profession in the 1950s faced more difficulties as women than they did as Jews. Today, Jewish women are found in all corners of the profession, from feminist and queer theory to administration, critical race studies, and beyond.

Myra Cohn Livingston
Both through her poetry and her teaching, Myra Cohn Livingston inspired children to explore the music of language. She eventually wrote more than twenty collections of as well as several books on writing poetry, serving as an inspiration for students to enjoy poetry.
Minnie Dessau Louis

Harriet Lowenstein

Esther Lowenthal
Esther Lowenthal’s long career teaching economics at Smith explored subjects from government spending and taxation to the theories of socialist economists.

Yeshivat Maharat
Founded by Rabba Sara Hurwitz and Rabbi Avi Weiss, Yeshivat Maharat is the first Orthodox rabbinical school to ordain women. Building upon expanding education and ritual roles for Orthodox women in America that began in the late twentieth century, themselves outgrowths of American feminism, as of 2021 Yeshivat Maharat had graduated over forty women who powerfully impact Orthodox and wider Jewish communities all over the world.

Selma Mair
Selma Mair was a German-born registered nurse who brought her education and devotion to the role of head nurse at the Sha’arei Zedek hospital in Jerusalem.
Judith Pinta Mandelbaum
Judith Pinta Mandelbaum was an important part of the Mizrachi Women’s Organization of America (American Mizrachi Women) from the 1930s until shortly before her death in 1977, by which time the organization was known as AMIT. She also achieved professional acclaim as an outstanding teacher and is remembered fondly as a woman with a wonderful sense of humor and a rich family life.

Ruth Barcan Marcus
Miriam Markel-Mosessohn

Alicia Markova
Dame Alicia Markova, Britain’s first and the first Jewish prima ballerina, combined amazing technique and personal strength with tremendous artistry to become one of the finest classical dancers of her generation. Through her touring and early recognition of the power of mass media, she was also one of ballet’s greatest ambassadors in the mid-twentieth century. Markova extended her legacy through choreography, teaching, and commitment to coaching the next generation of dancers.

Jessie Marmorston
Jessie Marmorston was a professor of experimental medicine, researching a stunning range of medical disciplines including immunology, endocrinology, psychoanalysis, and cardiology. Her research into hormone secretion led to breakthroughs in our understanding of the ways stress can contribute to heart attacks and certain cancers.

Judith Marquet-Krause
Judith Marquet-Krause was an archeologist who contributed her talents to early twentieth-century excavations of ancient cities across Palestine, most notably leading the excavation of Ai.

Henriette May
Henriette May was committed to the upbringing of children and care for needy adults. She was active as a board member and editor for Jewish newspaper Jüdischer Frauenbund starting in 1907, established a home for Jewish women teachers in Berlin, and was a prominent member of numerous welfare institutions.

Susan Maze-Rothstein

Yavilah McCoy
Medieval Ashkenaz (1096-1348)
The Jews of medieval Ashkenaz are known for their prolific rabbis and for the Ashkenazic customs that became characteristic of many European Jewish communities. During the High Middle Ages, the women in these communities had many important roles women within the family and in the communal, economic, and religious life.


